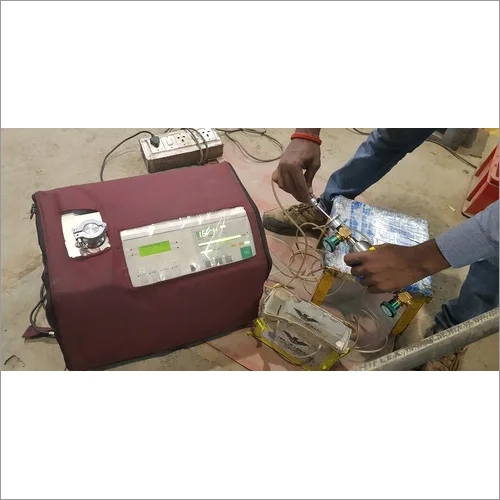
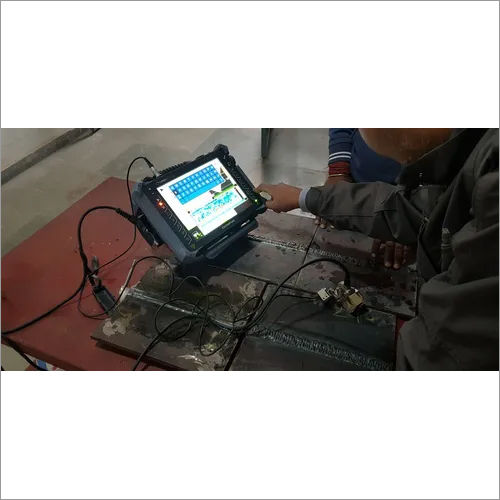
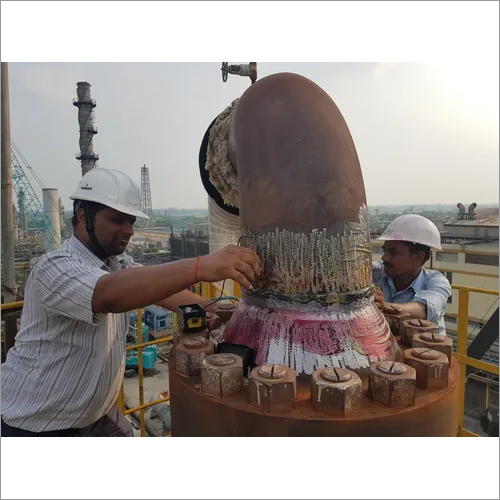
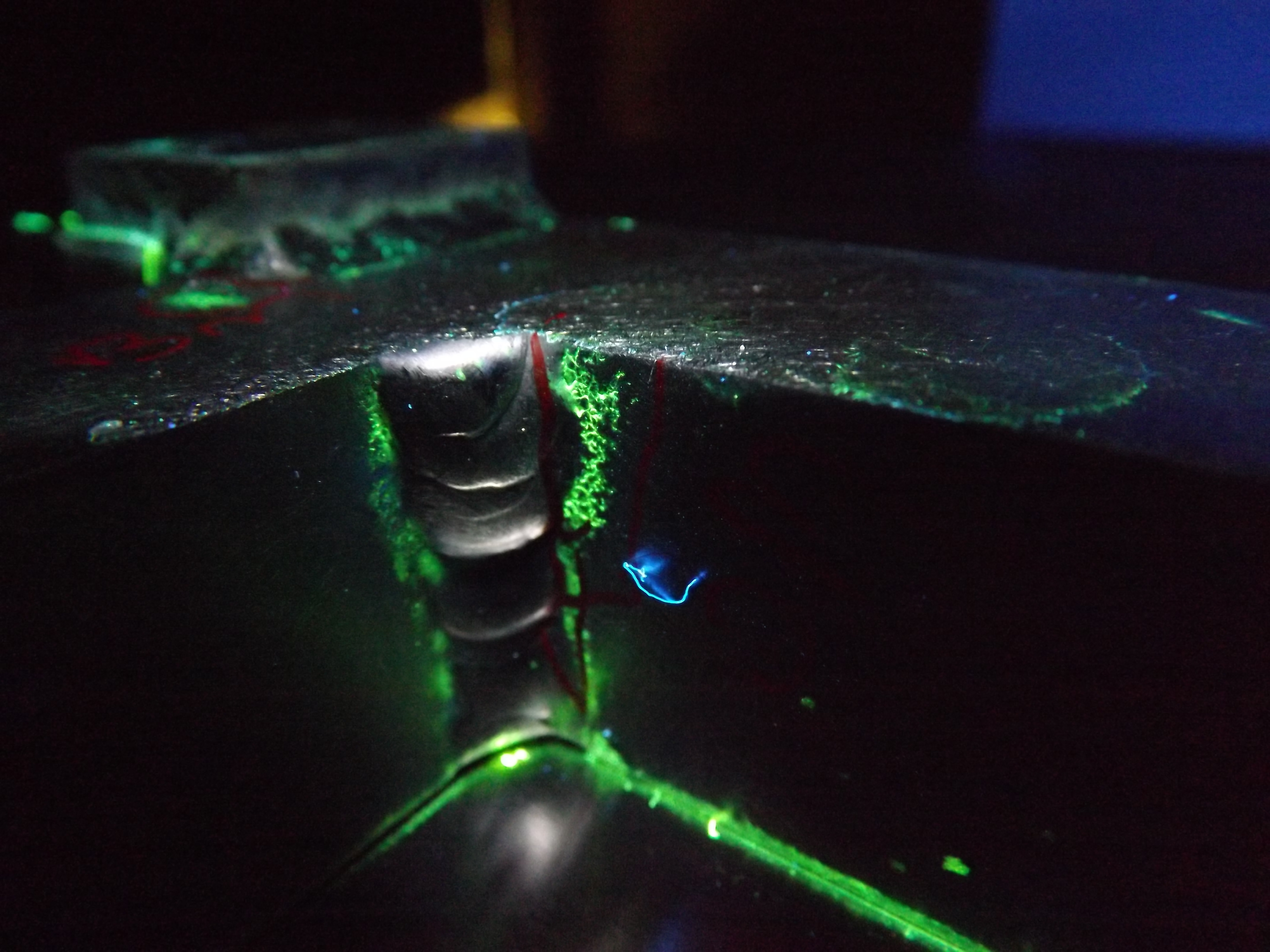
Liquid Penetrant Testing
Liquid Penetrant Testing Specification
- Material
- Liquid Penetrant (chemically formulated for non-destructive testing)
- Temperature
- Optimal working temperature: 10C to 50C
- Size
- Standard container sizes: 1 Litre, 5 Litres, 20 Litres (others available on request)
- Usage & Applications
- Detection of surface-breaking defects on ferrous and non-ferrous metals, ceramics, and non-porous materials. Widely used in metal fabrication, aerospace, automotive, and welding inspection.
- Weight
- Varies with container size
- Driven Type
- Manual
- Measuring Range
- Surface defect detection (visibility depends on flaw size and test surface)
- Interface
- Manual application (spray, brush, or immersion)
Liquid Penetrant Testing Trade Information
- Main Domestic Market
- North India
About Liquid Penetrant Testing
Liquid penetrant testing, also known as Dye Penetrant Inspection, is a widely used non destructive testing method that allows engineers to identify surface breaking defects in materials. It is a simple and cost effective way to detect small cracks, porosity, laps, and other discontinuities that are not visible to the naked eye. Liquid penetrant testing, also known as Dye Penetrant Inspection, is a widely used non destructive testing method that allows engineers to identify surface breaking defects in materials. It is a simple and cost effective way to detect small cracks, porosity, laps, and other discontinuities that are not visible to the naked eye.
The basic principle of liquid penetrant testing is to use a highly visible dye that is applied to the surface of the material being tested. The dye penetrates into any surface discontinuities by capillary action and then is removed from the surface. A developer is then applied to the surface, which draws the dye back out of the discontinuity and highlights its location on the surface. This method can be used on a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites.
The process of liquid penetrant testing involves several steps. First, the surface being tested must be cleaned thoroughly to remove any contaminants that could interfere with the testing process. Next, the penetrant is applied to the surface and allowed to soak in for a specified amount of time. Excess penetrant is then removed, and the developer is applied to the surface, which draws the penetrant back out of any surface discontinuities. Liquid penetrant testing has several advantages over other testing methods. It is easy to perform, requires minimal training, and can detect surface discontinuities that might be missed by visual inspection. However, it does have limitations. It cannot detect subsurface defects, and it can only detect defects that are open to the surface. Additionally, the penetrant materials used in this method can be messy and may require special handling and disposal.
In summary, liquid penetrant testing is a valuable tool for engineers and can be used to detect surface breaking defects in a variety of materials. It is a simple, cost effective, and reliable method that can be used in a variety of industries, including aerospace, automotive, and construction.
Product details
|
Place of Service |
Factories |
|
Time Duration |
2 to 3 Hours |
|
Technology |
Pentration |
|
Metal Type |
Ferrous Metal |
|
Mode |
Offline |
|
Service Type |
Testing |
|
Place of Service |
Factories |
|
Time Duration |
2 to 3 Hours |
|
Technology |
Pentration |
|
Metal Type |
Ferrous Metal |
|
Mode |
Offline |
|
Service Type |
Testing |
Versatile Detection for Multiple Industries
The high-sensitivity liquid penetrant is ideal for identifying both fine and coarse defects, serving applications in metal fabrication, aerospace, automotive, and welding inspections throughout India. Its compatibility with ferrous, non-ferrous metals, and ceramics ensures broad usability, making it a preferred choice for surface flaw detection.
Water-Based and Solvent-Based Formulations
Offering a choice between water-based and solvent-based penetrants enables users to pick a solution best suited to their operational requirements. Water-based products are non-flammable, while solvent-based variants possess a flash point above 65C, enhancing safety and flexibility in varied environments.
Ease of Use and Safe Handling
Manual application methods, such as spray, brush, or immersion, allow for straightforward implementation on inspection sites. Leak-proof, UN-approved packaging ensures safe transport, and the non-toxic composition assures user safety with standard personal protective equipment.
FAQs of Liquid Penetrant Testing:
Q: How do I apply Liquid Penetrant Testing products during inspection?
A: The liquid penetrant can be manually applied using a spray, brush, or by immersion, ensuring comprehensive coverage of the test surface for effective flaw detection.Q: What types of defects can high-sensitivity penetrants detect?
A: They are designed to identify fine and coarse surface-breaking flaws on metals, ceramics, and other non-porous materials, enhancing inspection for critical applications.Q: When should the penetrant be removed, and how is removability achieved?
A: After the required dwell time, the penetrant is removed using water for water-based formulations or solvent for solvent-based options, preventing residue and ensuring clear visual results.Q: Where should I store the liquid penetrant containers?
A: Containers should be stored in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight to maintain product efficacy and stability throughout the shelf life.Q: What are the benefits of selecting a formulation with bright red, fluorescent, or visible dye options?
A: Choosing between bright red, fluorescent, or visible dyes increases the visibility of defects during inspection, facilitating accurate and reliable detection across a range of environments.Q: Is the product safe to use, and what precautions are necessary?
A: The penetrant is non-toxic and non-corrosive, posing minimal health risk. Standard PPE should be worn during application as a general precaution.Q: What regulatory standards do these liquid penetrants comply with?
A: Products meet the requirements of ASTM E1417 and ISO 3452, ensuring reliable performance and acceptance in professional non-destructive testing practices.
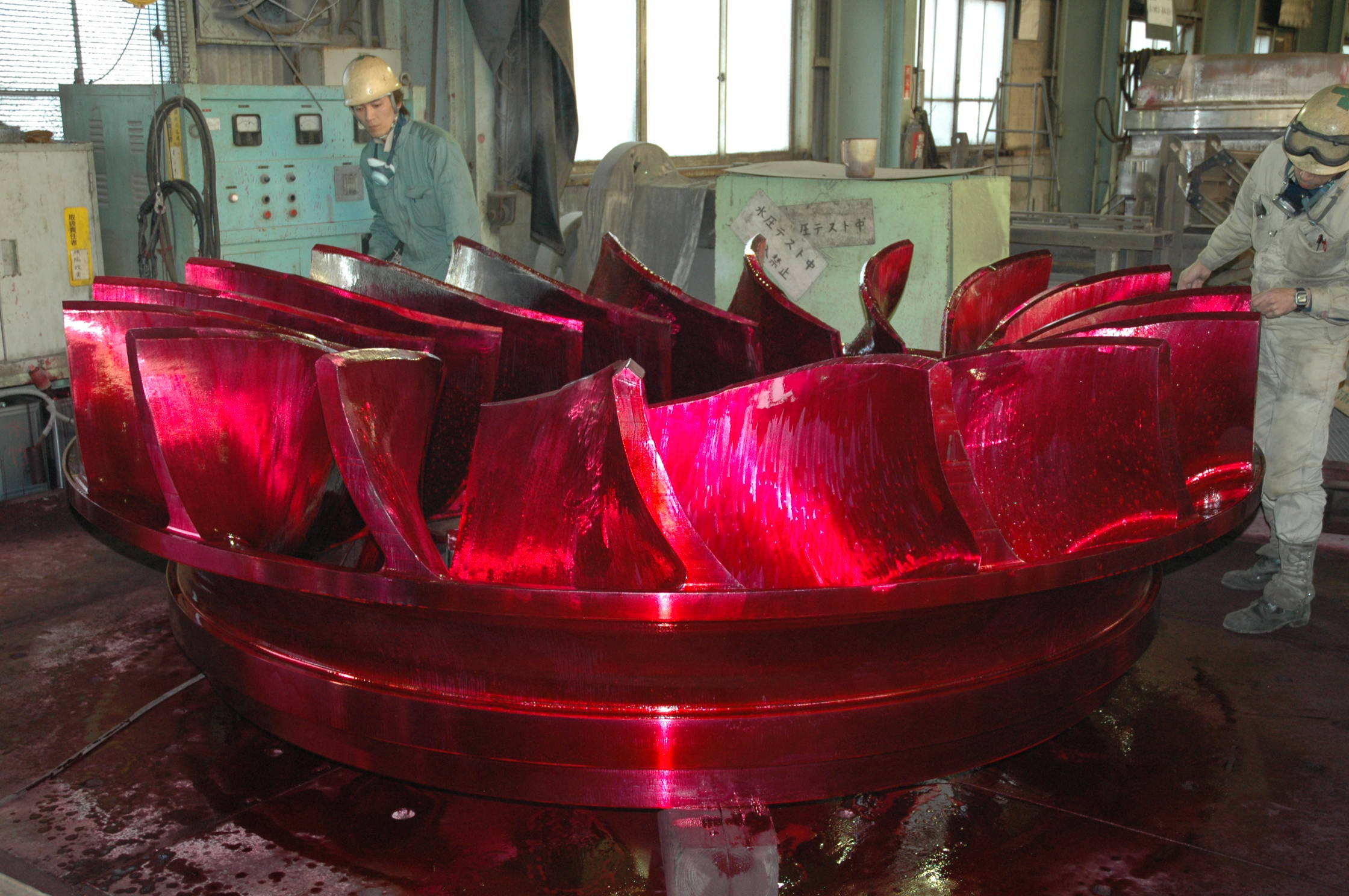

- Main Domestic Market
- North India

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in Non Destructive Testing Category
Positive Material Identification
Size : Handheld
Temperature : 0C to +50C
Display : Digital LCD Touch Screen
Frequency : 50/60 Hz
Usage & Applications : Positive Material Identification (PMI) in metals and alloys, including quality assurance and sorting
Power : LiIon Battery
Ultrasonic Thickness Measurement
Size : 150 mm x 74 mm x 32 mm
Temperature : 10C to 60C (operating)
Display : 4digit LCD
Frequency : 5 MHz
Usage & Applications : Measuring thickness of metals, pipes, tanks, and other materials
Power : 3V (2 x AA batteries)
Insitu Hardness Testing Services
Size : Portable
Temperature : 050 Degree Celsius
Display : Digital LCD Display
Frequency : 50 Hertz (Hz)
Usage & Applications : Hardness Testing of Metal Components On Site
Power : Battery Powered
Ultrasonic Testing
Size : Portable, Handheld Unit
Temperature : Operating: 0C to 50C
Display : Digital LCD Display
Frequency : 1 MHz 10 MHz
Usage & Applications : Flaw Detection, Thickness Measurement, Weld Inspection
Power : Battery Operated / Mains Powered
 |
INSPECTION & TESTING ENGINEERS
All Rights Reserved.(Terms of Use) Developed and Managed by Infocom Network Private Limited. |
 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese